Nutrition & Vitamins
WHY BANANAS ARE A SUPER BODY AND MIND FOOD
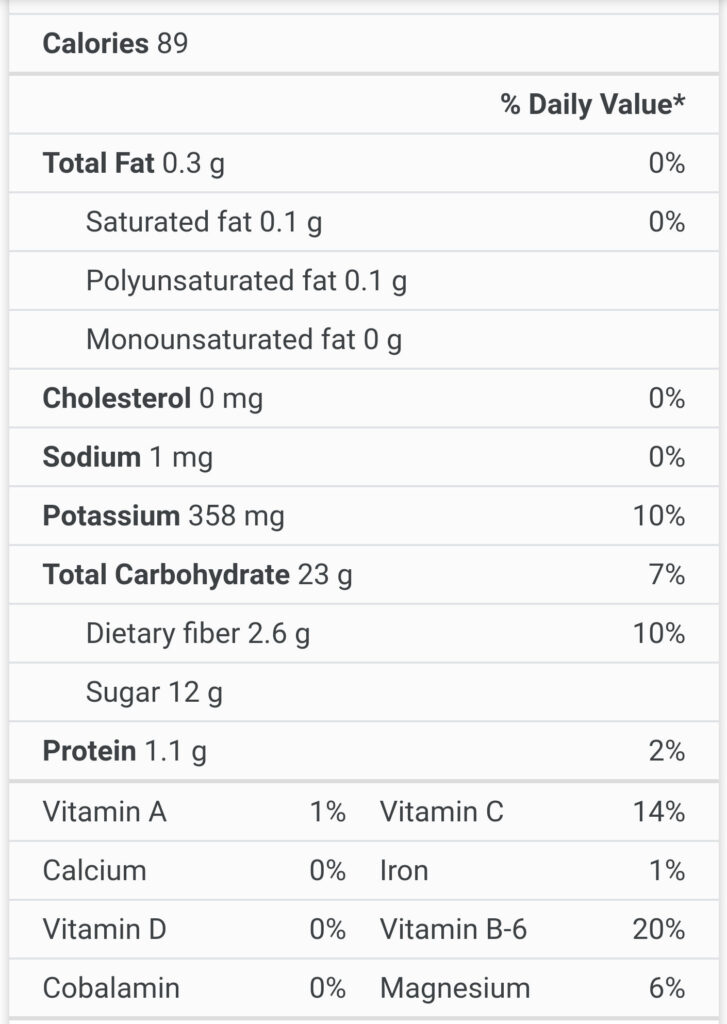
Bananas: Bananas are a good source of several vitamins and minerals, especially potassium, vitamin B6 and vitamin C.
Potassium: Bananas are a good source of potassium. A diet high in potassium can lower blood pressure in people with elevated levels and benefits heart health.
Vitamin B6: Bananas are high in vitamin B6. One medium-sized banana can provide up to 33% of the Daily Value (DV) of this vitamin.
Vitamin C: Like most fruit, bananas are a good source of vitamin C.
Pectin: Bananas are also a good source of other types of fibre, such as pectin. Some of the pectin found in bananas is water-soluble. When bananas ripen, the proportion of water-soluble pectin increases, which is one of the main reasons why bananas turn soft as they age. Both pectin and resistant starch moderate the rise in blood sugar after a meal.
Carbs: Bananas are mainly composed of carbs. Unripe bananas may contain decent amounts of resistant starch, which functions like fibre, aiding your gut. Bananas have a relatively low Glycemic Index (GI) of 42-58, depending on their ripeness. The GI is a measure of how quickly carbs in food enter your bloodstream and raise blood sugar levels. Banana’s high content of resistant starch and fibre explains their low GI.
Fibres: A high proportion of the starch in unripe bananas is resistant starch, which passes through your gut undigsted. In your large intestine, this starch is fermented by bacteria to form butyrate, a short chain fatty acid that appears to have beneficial effects on gut health.
Athletic Performance and Bananas
The unique mix of vitamins, minerals and low glycemic carbohydrates in bananas has made them a favourite among endurance athletes. Their easy portability, low expense and great taste also help support their popularity in this exclusive group.
A 2012 study of distance cyclists found that eating the equivalent of about one half a banana every 15 minutes of a three-hour race was just as good as keeping energy levels steady as drinking an equivalent amount of carbohydrate and minerals from a processed sports beverage. Bananas have long been valued by athletes for prevention of muscle cramps. Since bananas are a good source of potassium and since low potassium levels are known to contribute to risk of muscle cramps, it is logical to think about the potassium content of bananas as being the reason for fewer muscle cramps after the consumption of bananas. There is actually some recent research in support of this reasoning. In a recent study, consumption of one or two bananas prior to an hour of exercise was shown to keep blood potassium levels higher after the training.
Bananas can be used in all sorts of ways to make refreshing breakfasts, meals and desserts as well as being the ideal brain fit super food for mid morning and mid afternoon top up’s when the body and brain need feeding. See Fyffes Cookbook for some great recipe ideas.
